J01.0-4/J01.8-9
DESCRIPTION
Bacterial infection of one or more paranasal sinuses that occurs most often after a viral nasal infection or allergic rhinitis.
Bacterial sinusitis is characterised by:
- Deterioration of a common cold after 5–7 days.
- Headache.
- Purulent nasal discharge, especially if unilateral.
- Pain and tenderness over one or more sinuses.
- Nasal obstruction.
- Fever.
Note: Sinusitis is uncommon in children < 5 years of age, as sinuses are not fully developed.
GENERAL MEASURES
Consider HIV in recurrent sinusitis.
MEDICINE TREATMENT
Children ≤ 3 years of age
- Amoxicillin, oral, 45 mg/kg/dose 12 hourly for 5 days.
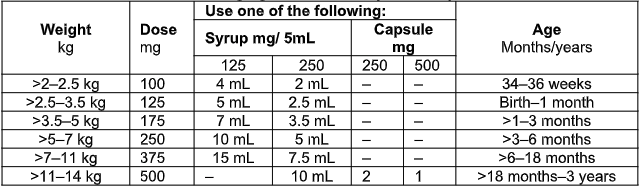
Children > 3 years of age
- Amoxicillin<, oral, 500 mg 8 hourly for 5 days.
Adults
- Amoxicillin, oral, 500 mg 8 hourly for 5 days.
Severe penicillin allergy (Z88.0)
Children
- Macrolide, e.g.:
- Azithromycin, oral, 10 mg/kg/dose, daily for 3 days. See paediatric dosing tool.
Children > 35 kg and adults
- Macrolide, e.g.:
- Azithromycin, oral, 500 mg daily for 3 days.
AND
- Oxymetazoline, nose drops, 2 drops in each nostril 6–8 hourly for not more than 5 days continuously.
- Children > 5 years of age: 0.025%
- Adults: 0.05%
AND/OR
- Sodium chloride 0.9%, nose drops, use frequently and in fairly large volumes.
Pain:
Children
- Paracetamol, oral, 10–15 mg/kg/dose 6 hourly when required. See paediatric dosing tool.
Adults
- Paracetamol, oral, 1 g 4–6 hourly when required.
- Maximum dose: 15 mg/kg/dose.
- Maximum dose: 4 g in 24 hours.
REFERRAL
- Fever lasting > 48 hours.
- Poor response > 5 days.
- Complications, e.g. periorbital cellulitis with periorbital swelling.
- Oedema over a sinus.
- Recurrent sinusitis.
- Meningeal irritation.