H66.9
DESCRIPTION
Inflammation of the middle ear characterised by:
- pain
- drum perforation
- loss of hearing
- fever in about half of the cases
- red bulging eardrum
- loss of the normal light reflex of the eardrum
Mild redness of the eardrum and rubbing the ear are not reliable signs.
GENERAL MEASURES
- Do not instil anything into the ear.
- Avoid getting the inside of the ear wet.
- Dry mop ear if discharge is present.
- Do not plug the ear with cotton wool, etc.
- Exclude HIV infection as a contributing factor for recurrent ear infection.
MEDICINE TREATMENT
Children
- Amoxicillin, oral, 45 mg/kg/dose 12 hourly for 5 days.
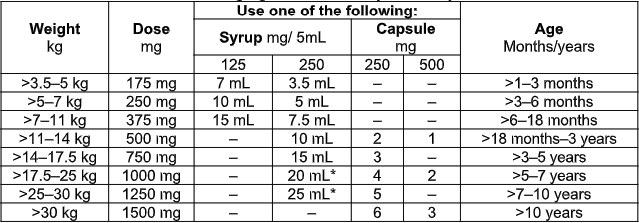
- LoIII [6]
- Review response after 5 days.
- If pain or discharge persists, consider alternative diagnosis and continue antibiotics for a further 5 days.
Adults
- Amoxicillin, oral, 1500 mg 12 hourly for 5 days.
Antibiotic treatment for those who have taken amoxicillin in the previous 30 day; or poor response to 10-day course of amoxicillin:
Children
- Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid oral, 15–25 mg/kg/dose of amoxicillin component, 8 hourly for 5-10 days.
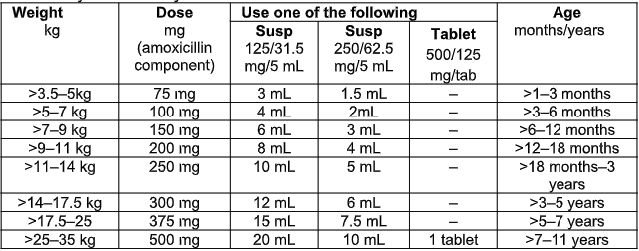
Children > 35 kg and adults
- Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, oral, 875/125 mg 12 hourly for 5 to 10 days.
Severe Penicillin allergy: (Z88.0)
Children
- Macrolide, e.g.:
- Azithromycin, oral, 10 mg/kg/dose, daily for 3 days. See paediatric dosing tool.
Children > 35 kg and adults
- Macrolide, e.g.:
- Azithromycin, oral, 500 mg daily for 3 days.
Pain:
Children
- Paracetamol, oral, 10–15 mg/kg/dose 6 hourly when required. See paediatric dosing tool.
Adults
- Paracetamol, oral, 1 g 4–6 hourly when required to a maximum of 4 doses per 24 hours.
- Maximum dose: 15 mg/kg/dose.
- Maximum dose: 4 g in 24 hours.
For patients with upper respiratory tract congestion, secondary to allergy: (T78.4)
- Non-sedating antihistamine, oral, e.g.:
- Cetirizine, oral, 10 mg daily for 10 days.
[LoE:II]10
For management of allergic rhinitis, see section 19.1: Allergic rhinitis.
REFERRAL
- Severe pain, fever or vomiting, not responding to treatment after 72 hours (if otoscopy confirmed) or after 24 hours (if otoscopy unconfirmed).
- Recurrent otitis media.
- Painful swelling behind the ear or tenderness on percussion of the mastoid.
- Suspected meningitis.